From Science Fiction to Reality: AI's Growing Impact
The U.S.-China tech rivalry intensifies as AI advancements shape the future, balancing automation with human empathy and ethical considerations.
AI - The Modern Assistant
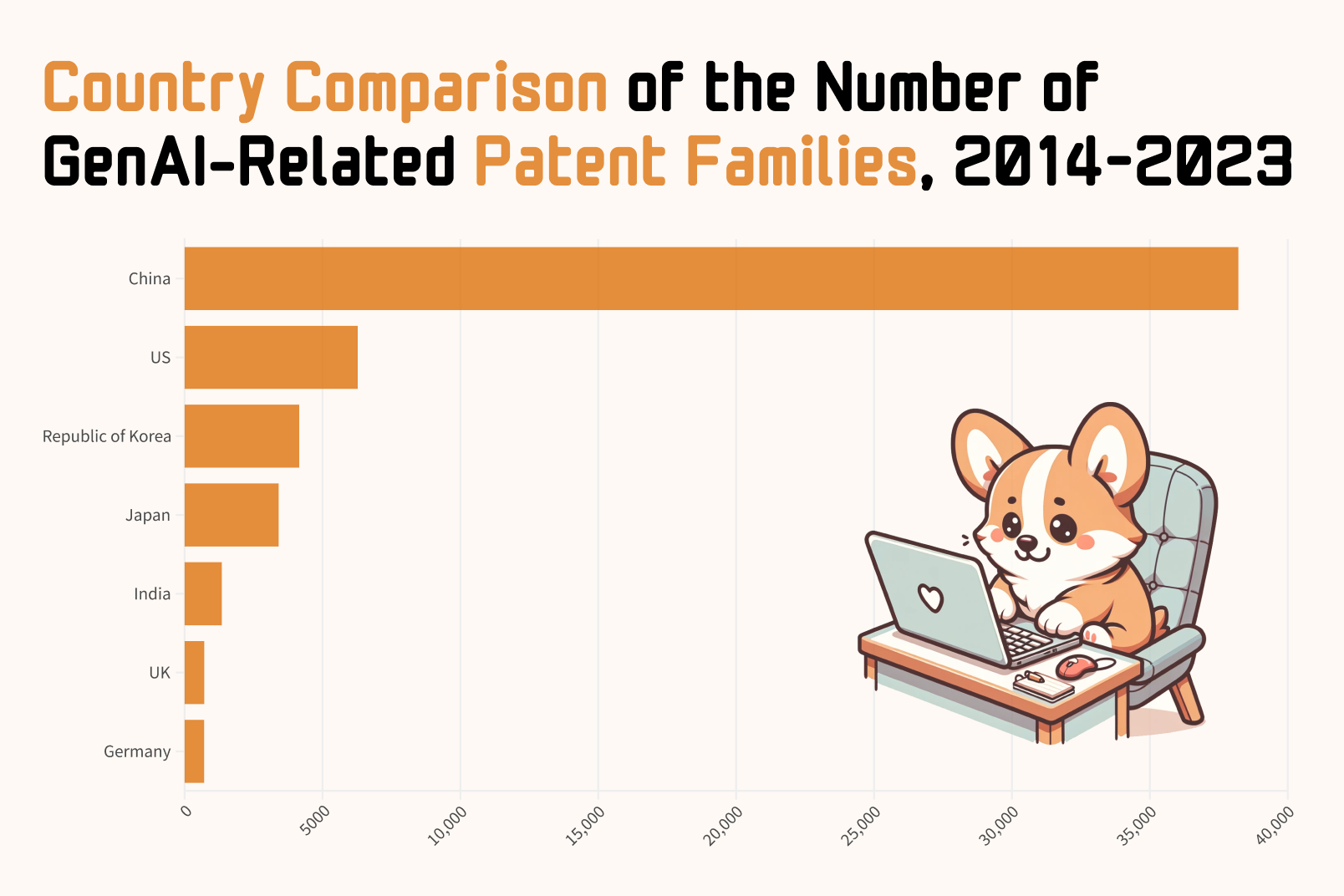
Alongside the trade war between the United States and China, initiated by Donald Trump's actions in 2018, these superpowers are also engaged in a technological battle across two main areas: semiconductors and artificial intelligence (AI). The US efforts to limit China's ability to produce and develop the most advanced chips are intensifying, as these components are crucial for AI advancement. Meanwhile, China is not backing down. According to the latest UN report1, from 2014 to 2023, Chinese entities patented over 38,000 AI-related inventions, which is more than six times the number of similar patents filed in the US during the same period. The Middle Kingdom is consistently striving to match American giants, particularly in the area of large language models (LLMs). Programs initiated by Chinese entities like Baidu and Alibaba2, along with a "three-year action plan"3, aim to propel the technological and economic development of domestic firms in the AI sector.
GenAI Patent Families by Country (2014-2023)
The Key to Humanity's Future
Many observers believe that this area of rivalry is crucial for the future of humanity, given its deep impact on global political dynamics. This puts us at a turning point in modern human history. From this international chaos, a new order will emerge, largely shaped by technology.
We no longer need to operate vast amounts of machinery as we did following the industrial revolution. Today, models can control the machines. But is there still a place for humans?
Humans are capable of quickly adapting to changing conditions. While biological limitations are undoubtedly our weakness, artificial intelligence can make these limitations more tolerable. For example, a recent project by researchers from the New Jersey Institute of Technology4 aims to develop robotic dogs that respond to their owners' commands using artificial intelligence, edge computing, and portable sensors to detect physiological and emotional stimuli. Robots like the Unitree Go2 will adjust their behavior based on the characteristics of the individuals they interact with. This innovation has applications in healthcare and home care, helping combat loneliness and supporting therapy or rehabilitation. Scientists also note that wearable devices, such as headphones, can monitor brain activity and microexpressions, allowing more precise interactions between robots and users.
Job Automation and Human Interaction
It is a fact that many strictly physical jobs can successfully be automated, but this does not necessarily mean millions of unemployed people. AI has many applications, but there are areas where it cannot replace human work or its capabilities are limited. Human-to-human interaction, deep understanding of cultural, social, and emotional contexts are domains where humans have an advantage. Hence, in the foreseeable future, jobs involving emotional or caregiving tasks, such as psychotherapy, physiotherapy, or elder care, seem safe. AI cannot replace the human touch and multi-domain understanding.
Another issue is ethics and morality, which are challenging to encode in AI systems. Human comparative advantages in the future job market also include making strategic decisions, crisis management, negotiations, and human resource management. These areas require specific skills and the ability to understand nuances and adapt to dynamically changing situations.
The Technological Revolution and the Paradigm Shift in Work
Among observers, there are concerns about the future of intellectual work. In this context, we should not fear artificial intelligence but rather strive to understand it. If we aspire to achieve higher competencies, it is worth considering which AI tools can be helpful in particular fields or positions. Speeding up task execution or analyzing large amounts of data in a short time is essential for achieving a competitive advantage5, which is a desirable goal for businesses. The key is optimization. By optimizing processes, we save time, and time is money. AI is an excellent assistant that makes work easier and allows us to think about various problems and solutions that were previously unreachable for humans engrossed in repetitive tasks or analyses limited by human thought horizons. At the current level of understanding, AI exhibits features of a highly useful assistant in both the scientific and business worlds. Ignoring such modern solutions today guarantees a loss in the future to those who are currently dedicating their attention and time to understanding the technologies of tomorrow.
Improving Life Quality with AI
Optimizing work can also contribute to improving the quality and length of human life. For instance, in the medical profession, faster disease diagnosis or effective treatment modification can positively impact the illness process and improve the everyday functioning of patients. This is evidenced by a recent study published in the journal "Translational Vision Science & Technology"6, which describes how advanced imaging technologies and artificial intelligence have enabled the automation of diagnosing and classifying multiple sclerosis.
Collaboration in AI Research
In the context of the collaboration between the scientific community and big tech, it's worth mentioning the recently announced partnership between OpenAI and Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL)7. This partnership aims to evaluate the capabilities of AI models like GPT-4o in real-world laboratory conditions, including their ability to support biological research through multimodal functions such as vision and voice. Scientists will concurrently investigate the safety profile of using artificial intelligence in advanced biosciences research. The growing role of AI in science will likely push research boundaries beyond the reach of currently available tools. Consequently, humanity stands to gain solutions necessary to overcome our biological weaknesses.
Latest AI News
It is commonly believed that the vacation season is a period of some slowdown in many industries, mainly due to numerous trips and a general atmosphere of relaxation in favorable weather conditions. This period is referred to as the "cucumber season" in Poland. However, such a phenomenon is not observed among tech giants. On the contrary, July was brimming with exciting news from global AI leaders.
In mid-July, OpenAI announced the introduction of GPT-4o mini8, a new, economical AI model designed to expand the availability of AI-based applications by lowering costs and delays. GPT-4o mini achieves 82% in the MMLU test, outpacing other models in chat preferences and being significantly cheaper than previous models, including GPT-3.5 Turbo.
AI Model Evaluation Scores Across Benchmarks
GPT-4o mini supports text and vision, and in the future, it will also handle text, graphic, video, and audio inputs and outputs. The model has a context window of 128,000 tokens and supports up to 16,000 output tokens per request. In comparative tests, it outperformed other small models in tasks requiring reasoning, mathematics, and coding, as well as in multimodal reasoning.
On July 23, Meta presented its most advanced AI model, Llama 3.1 405B9, which is a true competitor to proprietary models like Claude 3.5 Sonnet from Anthropic and GPT-4 from OpenAI, as confirmed in numerous experiments. With an open license, Llama 3.1 has the potential for wide application and further development by users, unlike the competition. The open-source concept and the fact that the latest model comprises 405 billion parameters make it the world's largest open-source LLM model. Users will be able to use this versatile tool to generate texts, solve mathematical problems, and code, among other things. Its multilingual support and integration with Meta applications like Facebook, Instagram, Messenger, and WhatsApp make Llama 3.1 an exceptionally attractive assistant for users. However, not everyone will have access to it.
Meta announced that it will not introduce its upcoming multimodal AI model in the European Union due to regulatory concerns10. This means European companies will be unable to use this model, even though it is available under an open license. Recently, the EU finalized compliance deadlines for AI companies under the new AI Act, which requires adaptation to copyright, transparency, and AI application regulations by August 2026. Meta's decision is similar to an earlier move by Apple, which also excluded the EU from its Apple Intelligence rollout due to concerns related to the Digital Markets Act. Meta has also halted plans to release its AI assistant in the EU and generative AI tools in Brazil due to data protection compliance issues.
The day after Meta's model release, French competitor Mistral AI announced the release of Mistral Large 211, the latest version of its flagship model. The new version offers significant improvements in code generation, mathematics, and reasoning compared to its predecessor. Moreover, in comparative tests, it outperformed the Llama 3.1 model in coding and mathematics. It supports several languages, including French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Arabic, Hindi, Chinese, Japanese, and Korean, and among the 80 coding languages it supports are Python, Java, C, C++, JavaScript, and Bash.
Performance vs Model Size: Code & Math Tasks
Key Developments in AI
Among the recent key events in the AI world, we must also highlight the success of MIT researchers who introduced GenSQL, a generative AI system for databases12. It allows users to perform complex statistical analyses on tabular data with just a few keystrokes. This new tool is useful for predictions, anomaly detection, estimating missing values, correcting errors, or generating synthetic data. Moreover, it automatically integrates a tabular dataset with a generative model probabilistically, which considers uncertainty and adjusts its decisions based on new data. It can also be used to create and analyze synthetic data that reflect real data in the database, which is especially helpful when sensitive data cannot be shared, such as patient medical records, or when real data is scarce. This tool opens new possibilities in tabular data analysis, and its use can accelerate research and decision-making processes in many fields.
Be the Beneficiaries of This Race
AI industry giants are intensely competing and continually enhancing their products to gain a technological edge. Users benefiting from this rivalry consequently achieve competitive advantages in their fields. Language models have applications in many areas, from customer service to data analysis and content creation. From the wide array of available services and products offered by companies specializing in AI development, practically every interested party can find a useful tool that will support their professional duties. But work is not the only thing that matters. AI also finds applications in private life. Companies frequently release many interesting tools that enhance applications we use daily for personal purposes. Thus, it is worthwhile to keep an eye on market trends and innovations to not only become more efficient workers but also to compress the time spent on everyday tasks.
At the same time, it is essential to remember that technology development brings new challenges related to ethics and regulations. The mentioned AI Act, introduced by the European Union, constitutes a significant barrier to AI development in the European market. EU regulations, which limit access to modern technologies and advanced tools, may slow this sector's development and negatively impact the EU economy's competitiveness in the global market.
Sources
- ↑ WIPO Technology Trends 2019 - Artificial Intelligence
- ↑ Chinas tech giants plan ChatGPT clones and Beijing is watching closely
- ↑ China: Generative AI Measures Finalized
- ↑ Institute for Future Technologies partnership trains robotic dogs to respond to their masters
- ↑ The Top 100 Gen AI Consumer Apps
- ↑ AI-Enabled Automated Detection of Multiple Sclerosis from Retinal Fundus Photographs
- ↑ OpenAI and Los Alamos National Laboratory Work Together
- ↑ GPT-4o mini - Advancing cost-efficient intelligence
- ↑ Introducing Llama 3.1 - Our most capable models to date
- ↑ Meta stops EU roll-out of AI model due to regulatory concerns
- ↑ Mistral Large 2
- ↑ MIT researchers introduce generative AI for databases
